How to Calculate Time and a Half: Overtime Pay Guide

Struggling with overtime calculations? Many small business owners underpay or overpay employees due to time and a half confusion, risking fines up to $1,000 per violation under FLSA. Get it right with this guide.
What Is Time and a Half?
Time and a half means paying non-exempt employees 1.5 times their regular hourly rate for hours worked over 40 in a workweek. This stems from the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), covering most U.S. hourly workers.
Federal law mandates this for overtime, but some states like California require daily overtime after 8 hours. According to the U.S. Department of Labor, non-compliance affects millions of workers annually.
Who Qualifies for Time and a Half?
Only non-exempt employees qualify. Exempt workers (executive, administrative, professional) earning above $35,568 annually ($684/week as of 2025, post-rule vacatur) don't get overtime.
Hourly employees are typically non-exempt. Salaried non-exempt get overtime based on their regular rate equivalent.
Small businesses: Classify correctly to avoid DOL audits. Misclassification is the top overtime violation.
Federal and State Overtime Laws
FLSA requires time and a half after 40 hours/week. Key 2025 notes:
- Salary threshold reverted to 2019 levels after 2024 rule blocked.
- States like CA, NY require daily OT (after 8-10 hours/day).
- No federal daily OT, but 7 states mandate it.
| Requirement | Federal (FLSA) | Example States (Stricter) |
|---|---|---|
| OT Trigger | >40 hrs/week | CA: >8 hrs/day or >40/week |
| Rate | 1.5x regular | Same, or 2x on 7th day (CA) |
| Exempt Salary | $35,568/year | Higher in some states |
Always check state laws via DOL website.
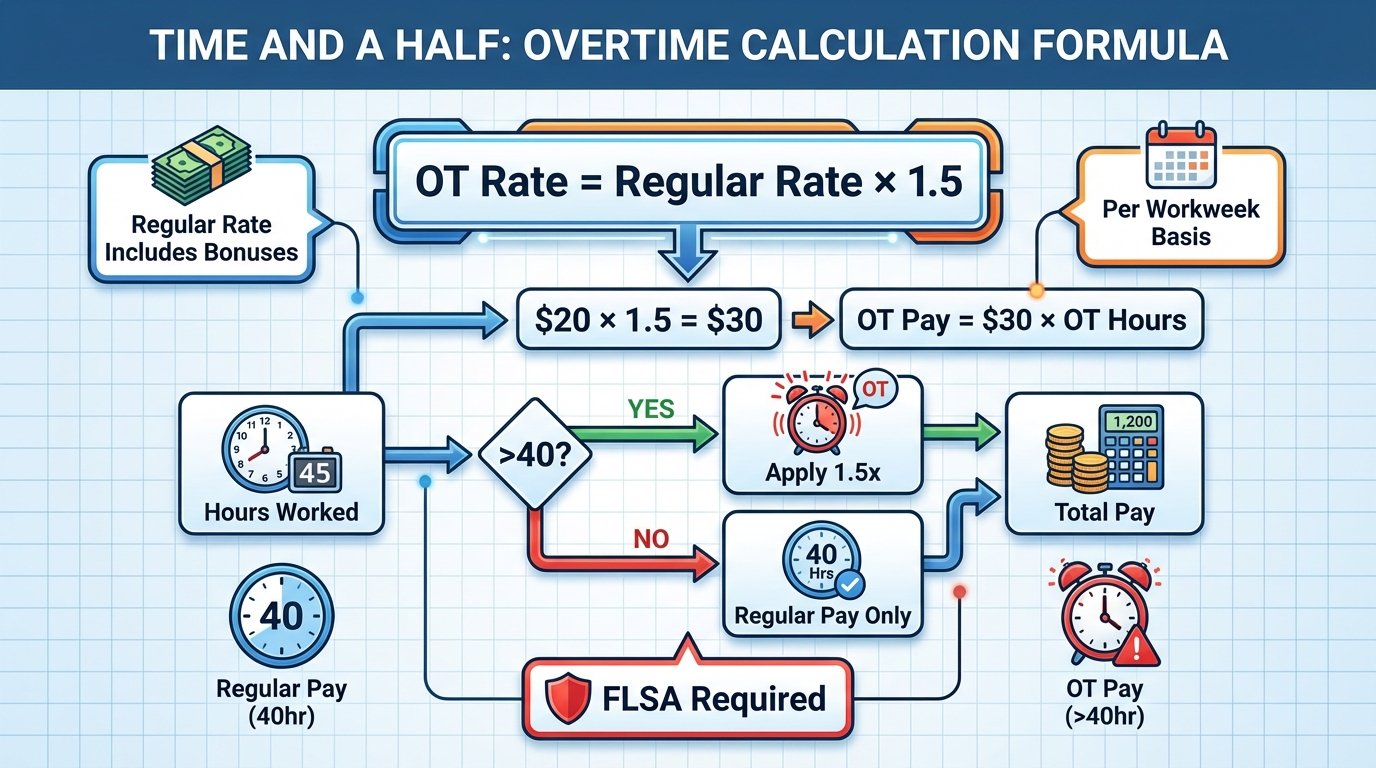
How to Calculate Time and a Half: Step-by-Step
Follow these steps for accurate payroll.
Determine Regular Hourly Rate
Include base wage plus non-discretionary bonuses/shift differentials divided by total hours.
Example: $20/hr base + $200 weekly bonus / 40 hrs = $25 regular rate.
Add to Regular Pay
Total pay = (regular rate x 40) + OT pay.
Real-World Calculation Examples
| Scenario | Regular Rate | Reg Hrs | OT Hrs | OT Rate | Total Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Weekly | $15 | 40 | 5 | $22.50 | $697.50 |
| With Bonus | $20 (+$100 bonus/40hrs = $22.50 reg) | 40 | 10 | $33.75 | $1,012.50 |
| Salaried Non-Exempt ($800/wk /40 = $20/hr) | $20 | 35 | 10 | $30 | $950 |
BLS data shows average 3.6 OT hours/week across industries.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Wrong regular rate: Exclude bonuses? Fines follow.
- Averaging hours: Calculate per workweek, not pay period.
- Off-clock work: Training, travel counts.
- Exempt misclassification: Review duties test.
- State ignorance: CA daily OT trips up many.
DOL recovered $238M in back wages last year.
Key Takeaways
- Time and a half = 1.5x regular rate after 40 hrs/week (FLSA).
- Include all pay in regular rate.
- Check state laws for daily OT.
- Use tools like PineBill for compliance.
- Audit classifications annually.